CNC machines are tried and true in metal machining and metalworking. They’re even more resourceful when manufacturers use them to automate deburring and finishing. But for some jobs, using a CNC machine for these processes is harder to manage and less efficient than alternatives, such as using a robotic arm with Xebec ceramic fiber brushes.
The market for industrial robotics is continually growing and is expected to reach $32.5 billion by 2028. Robots have already proven themselves in various manufacturing roles. Deburring and finishing are some of the latest functions to benefit. With robots, manufacturers can automate these processes for parts and products that aren’t as well-suited to deburring and finishing on a CNC machine. Additionally, robots can cost significantly less compared to CNC machines depending on their size.
With robotics now on the table, manufacturers must determine the best route to automate deburring and finishing at their facilities. It’s best to consult with an expert, such as Xebec’s deburring and finishing pros, to ensure you make the investment with the best returns and design the optimal system for your needs. Our reps enjoy working with manufacturers early in the process, to help develop the process to achieve your surface finish requirements.
In the beginning, it helps to have a primer. Here, we’ll compare the advantages and disadvantages of assigning these processes to CNC machines versus robotic arms.
What does a robotic deburring process involve?
Using collaborative robotics within a CNC creates highly precise and efficient manufacturing systems. The collaborative robots use computer-programmed instructions to control the movement of tools and components within the CNC, automatically performing complex, repetitive tasks with precision and consistency.
With the right tools, CNC robots can perform a wide range of operations including milling, drilling, cutting, deburring, finishing, and assembly that meets strict Ra requirements. Industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical device manufacturing can benefit from the high production, high quality benefits of collaborative robots within a CNC.
To streamline the process, the industrial robotic arm grabs the first tool in the sequence, does the task, drops the tool off and moves on to the next tool in the sequence. When you use a Xebec ceramic fiber brush to finish off the part with a robot, it makes the job more streamlined as the Xebec brush completes deburring and finishing at once.
Robots can be programmed to grab the parts themselves, move them out of trays and into machines, pick them up, turn them, and place them on other trays to send along – all with no human involvement. For the deburring process, such tool-and-part manipulation can involve two robots. This decreases the likelihood of error by reducing “touches”.
>> Xebec Guide for CNC Precision Manufacturing: Overcome Obstacles to Success
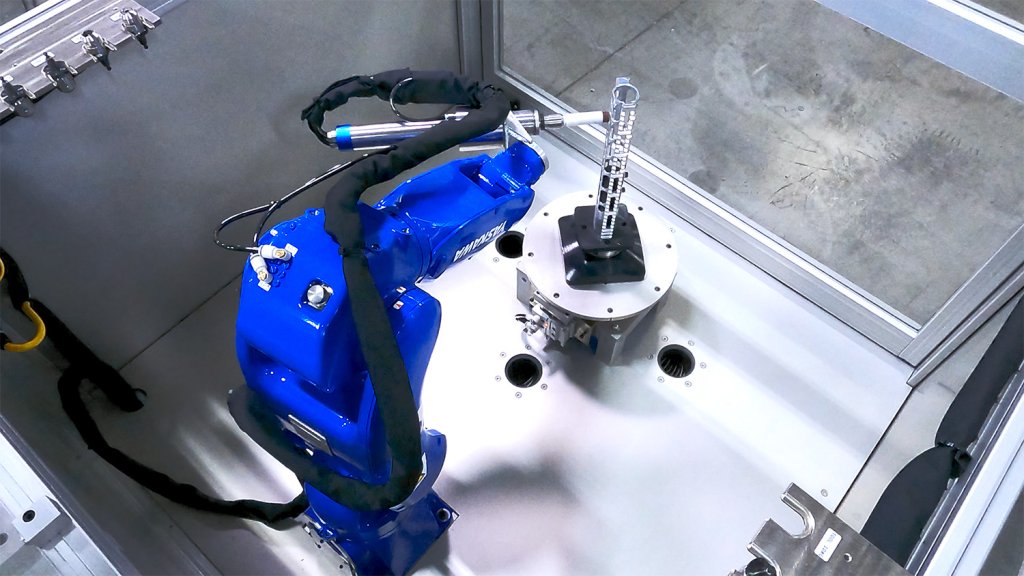

Deburring within Robotic Cells
Manufacturers who do not have time to introduce a deburring process to the cycle time in their CNC machines can implement collaborative robots in adjacent cells as an excellent alternative to help address inefficiencies in secondary operations.
Collaborative robots can be placed in a separate cell introduced specifically for deburring and finishing processes. Some collaborative robots may have the robot lift parts off a cart and into the cell where the part is then finished robotically. Other options have operators who manually load the parts onto the stand and then are finished by the robot.
Collaborative robots can deburr and finish parts at a constant speed with a constant force. They can work a repeatable path every time, and when paired with Xebec ceramic fiber brushes, deliver consistently high quality results. Using a collaborative robot programmed with Xebec brushes allows operators to set up the program, ensure the operation is going correctly, and proceed with unattended production.
The robotics company is typically responsible for developing the process and programming for the manufacturer. Xebec’s reps often work closely with both in this phase as we did with Ellison Technologies on automated burr removal and surface finishing of part using a Yaskawa GP8 industrial robotic arm with Xebec ceramic fiber brushes in a RoboBurr Workcell.
Robotic vs. CNC deburring and finishing
While robots cannot mill a part out of a block of metal, both CNC machines and robotics can be paired with automated deburring methods. And both tend to perform better than manual deburring methods. When the choice is between the two, the right option isn’t always immediately apparent.
High-Touch vs Plug ‘n’ Play
With a CNC machine, you need an operator and a programmer. And in many cases, parts must be switched out, flipped or moved from one CNC machine to another. There may be two to four machines involved in the manufacturing of one part, each performing a different machining process.
With robots, once the programming is complete, the arm is put in place and you essentially “press play.” A robot could deburr and finish in a single cell, which is economical both financially and in terms of space in a shop. It also frees up operators to run other machines and perform other tasks.
Hands-on vs. Hands-off
When a CNC machining process calls for transferring parts, there’s a higher risk of accidents, ergonomic injuries and damage to equipment and parts. The more times you touch a part, the more likely you are to damage it or injure yourself. Transferring usually involves fixturing a part over and over, increasing the potential for scratches, snags, misplacement and missed burrs – all of which affect the success of the operation. These incidents lead to scrap, rework and more frequent quality control inspections. Transferring is especially problematic for parts that are heavy or have tight tolerances.
Unlike with a CNC machine, transferring parts between machines for the deburring and finishing steps isn’t an issue with a robotic arm because the part remains in the same cell, which prevents part damage and operator injuries.
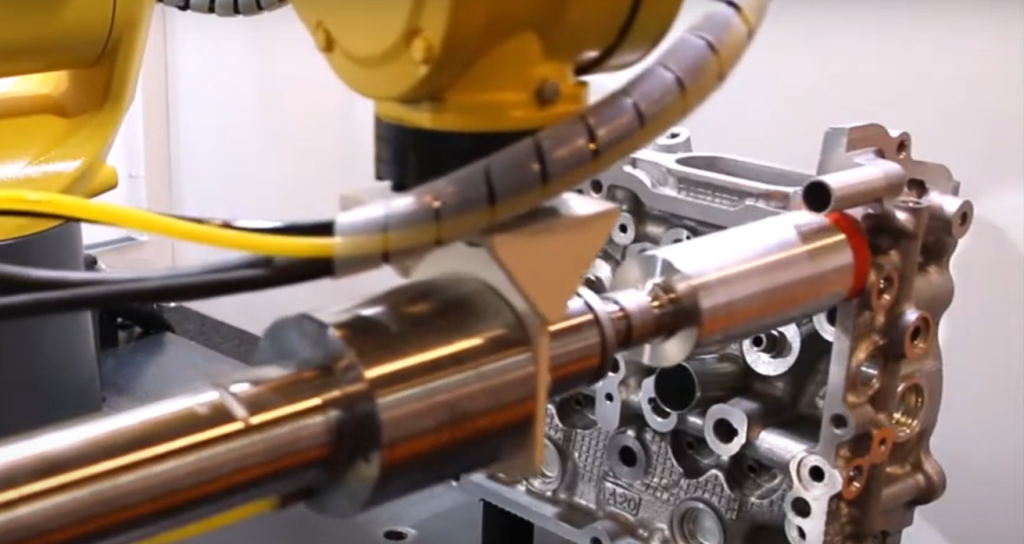

Fixed vs. Flexible
In CNC machines, tools work on a fixed, secured part. For instance, Xebec ceramic fiber brushes are programmed to work the part in the machine. And an operator needs to manipulate the part and secure it in place.
In the robotic process, industrial robotic arms can grab and move the part as well as the tools if programmed to do so. The tools the robot needs are available in a programmed sequence and an operator doesn’t have to intervene to move and fixture the part or tools.
Additionally, robots are suited for hard-to-reach areas and complex paths. They have superb maneuverability, with ranges up to seven axes, and can easily approach from many angles, orienting to the part as needed.
Accuracy vs. Repeatability
CNC machines excel in accuracy, which is critical in metalworking. They have greater rigidity compared to most robots. However, robots are gaining in this area and can be reliably accurate when programmed and applied correctly.
Robots excel in repeatability, another critical capability in the industry. The robot will do as it is programmed to do – without human touch. There is less opportunity for human error in the equation. For instance, a human operating a crane cannot achieve exact placement. Robots achieve precision in placement down to .002”.
In addition, robots don’t have bad days, miss their mark or accidentally overwork parts. If you’re using a manual deburring and finishing process today, consider the consistency and repeatability you can achieve by automating the process. Whether you rely on a robot or CNC for deburring, using Xebec tools ensures high-quality, dependable output.
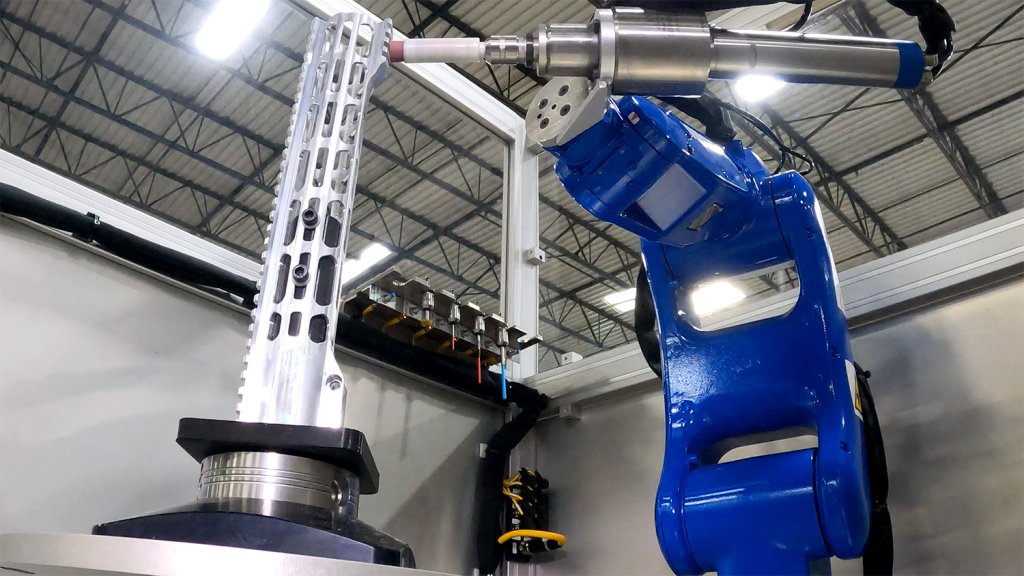

How Robotics and Collaborative Arms Complement CNC Work
Robotics and collaborative arms (cobots) are increasingly used alongside CNC machines to improve workflow efficiency and handle repetitive tasks that are less suited for traditional CNC systems. By combining the precision of CNC machining with the flexibility of robotics, manufacturers can achieve optimal results in part production and surface finishing.
- Loading and Unloading Parts: Robotic arms can be programmed to pick up raw parts, load them into CNC machines, and unload finished parts. This automation reduces downtime between machining cycles and minimizes labor costs.
- Tool Changes and Part Manipulation: In advanced setups, robotic arms can assist CNC systems by changing tools or reorienting parts. For complex geometries, cobots can also manipulate parts mid-process, reducing the need for manual intervention.
- Improved Machine Utilization: By automating secondary processes such as deburring and surface finishing with a robotic arm in the same work cell, manufacturers can maximize CNC machine uptime.
Robotic Deburring and Finishing Applications in Metal and Material Processing
Robotic arms excel at automating deburring and surface finishing processes across various materials. Applications include:
- Automotive Industry: Robotic deburring systems handle engine components, gears, and transmission parts with high precision, ensuring consistency in tight tolerance applications. Xebec ceramic fiber brushes are ideal for deburring complex engine components without damaging critical surfaces.
- Aerospace Industry: Complex metal alloys used in aerospace components benefit from robotic finishing, which provides consistent and precise edge and surface treatment.
- Medical Device Manufacturing: Robots ensure uniform deburring and finishing of stainless steel and titanium components, such as implants and surgical tools, where safety and precision are paramount.
- General Metal Fabrication: From sheet metal parts to castings, robotic deburring and polishing systems allow manufacturers to improve throughput while achieving quality finishes.
- Non-Metal Materials: Robotic deburring is also effective on plastics, composites, and ceramics, where gentle, controlled finishing processes are necessary to avoid material damage.
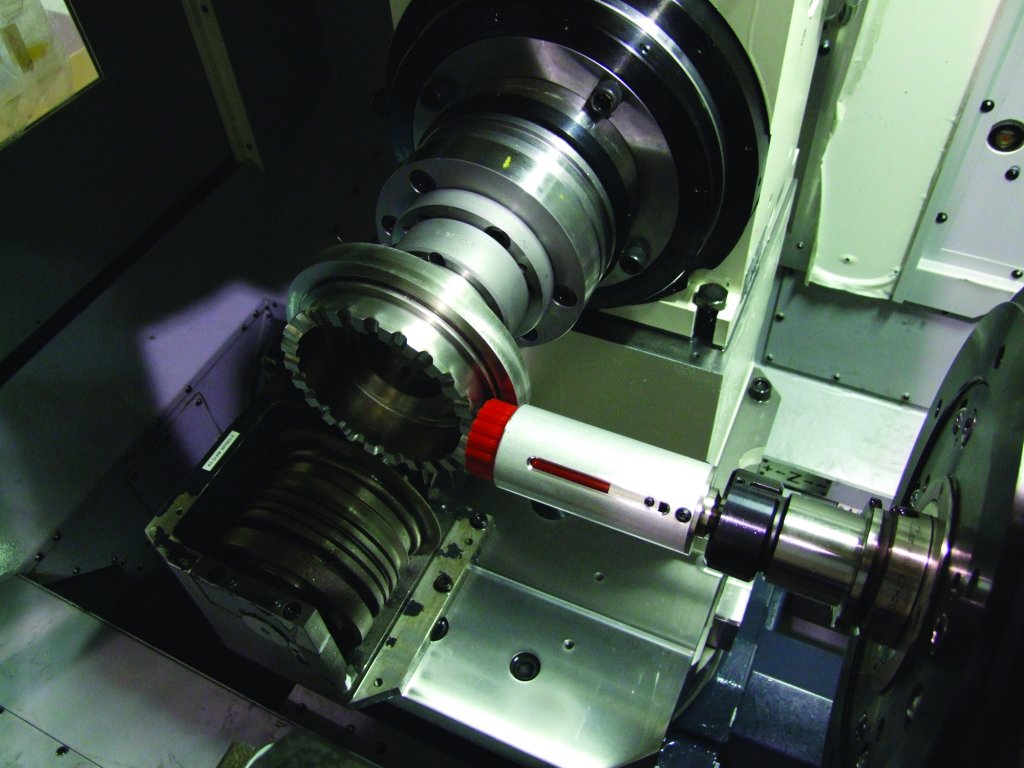

Collaborative Arms (Cobots) in Deburring and Finishing
Collaborative robots (Cobots) are designed to work alongside human operators safely and efficiently. These systems are particularly valuable for smaller manufacturers or environments with limited space. Some of the benefits of using cobots in your CNC machining operations:
- Flexibility for Low-Volume, High-Mix Production: Cobots excel in handling variable part types and smaller production runs where CNC machines or full industrial robotics may be too rigid.
- Ease of Programming: Cobots can be quickly reprogrammed for different deburring and finishing tasks, making them ideal for manufacturers handling custom or prototype work.
- Enhanced Safety: Cobots are equipped with sensors and safety features, allowing them to work in close proximity to humans, unlike traditional industrial robotic arms.
For example, a small machining shop can integrate a cobot equipped with Xebec ceramic fiber brushes to handle final deburring on aluminum alloy parts. Operators could then oversee production while the cobot performs repetitive finishing work, increasing efficiency without compromising safety.
Integrating Robotics for Lights-Out Manufacturing
Lights-out manufacturing refers to fully automated production environments that require little to no human intervention. Combining CNC machines with robotics for deburring and finishing enables:
24/7 Operation: Robots can run processes like deburring continuously, improving production capacity. Learn how to increase capacity and production due to consistency, reliability and speed – even while running lean with Xebec.
Reduced Labor Costs: By automating secondary tasks, operators have time to focus on quality control or other skilled roles. Learn how Xebec frees up skilled labor to perform other tasks.
Consistency and Quality: Robotic arms ensure repeatability, minimizing defects and improving overall product quality. Learn how achieve consistent quality with by embracing the future of the CNC machining industry with Xebec.
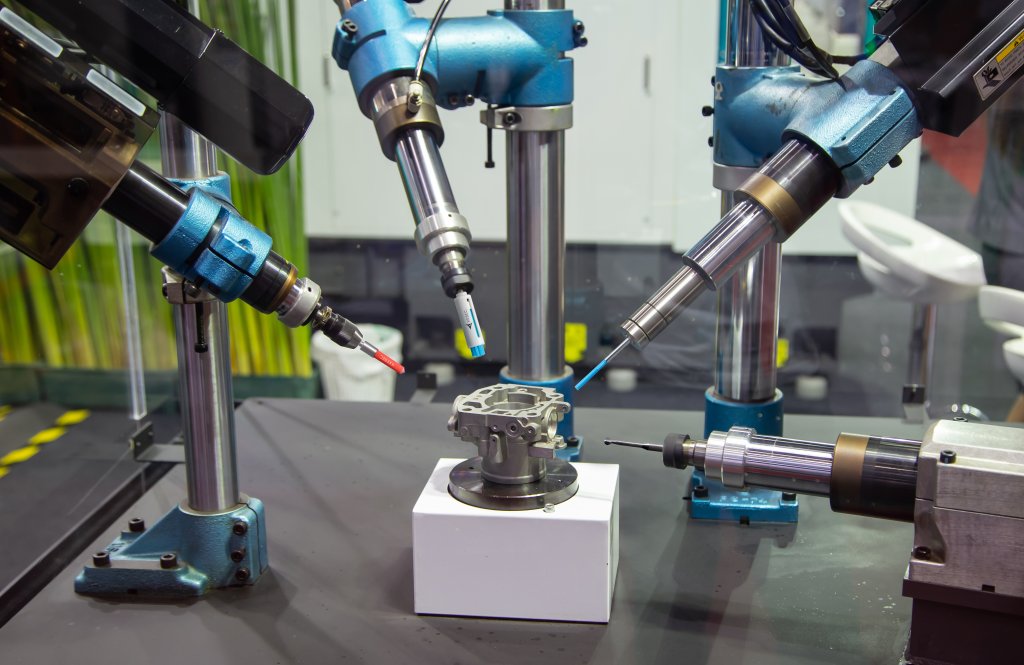
Which automated deburring method is right for you?
Automated deburring and finishing, whether with a CNC machine, robotic arm or cobot can greatly improve results and output from manual methods. No matter which method, automating with Xebec ceramic fiber brushes can improve safety and help manufacturers optimize their workforces.
>> How to Calculate the ROI on Automated Deburring with Xebec
At Xebec Deburring Technologies, our reps have a wealth of experience in a range of industries and manufacturing environments. We can help you identify the perfect solution for your application. Contact us to learn more and we can discuss your options.






